Computer System: A Breakdown
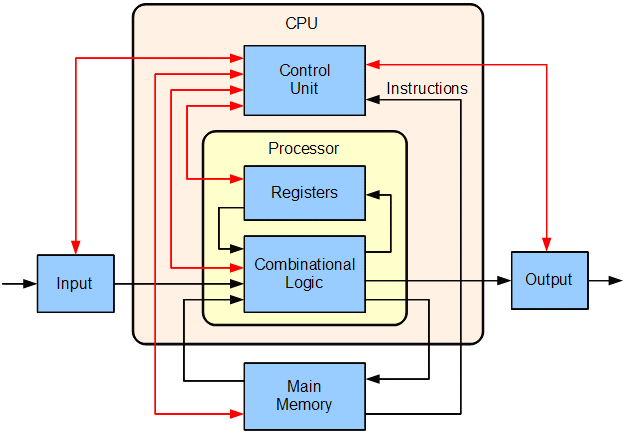
A computer system is a collection of hardware and software components that work together to process information. It typically consists of a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices.
Hardware Components of a Typical Computer System
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The "brain" of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory:
Stores data and instructions for the CPU to access. It includes: - Primary Memory (RAM): Volatile memory that stores data temporarily while the computer is running.
- Secondary Memory: Non-volatile memory that stores data permanently, such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical drives.
- Input Devices: Devices that allow users to enter data into the computer, such as keyboards, mice, scanners, and microphones.
- Output Devices: Devices that display or output data from the computer, such as monitors, printers, and speakers.
- Motherboard: A printed circuit board that connects all the components of the computer system.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Provides electrical power to the computer system.
- Expansion Cards: Additional components that can be inserted into the motherboard to enhance the computer's capabilities, such as graphics cards and network cards.
These are the essential components of a typical computer system. The specific configuration can vary depending on the intended use and performance requirements.





0 Comments